Accelerated Vector Search: Approximating with RAPIDS RAFT IVF-Flat
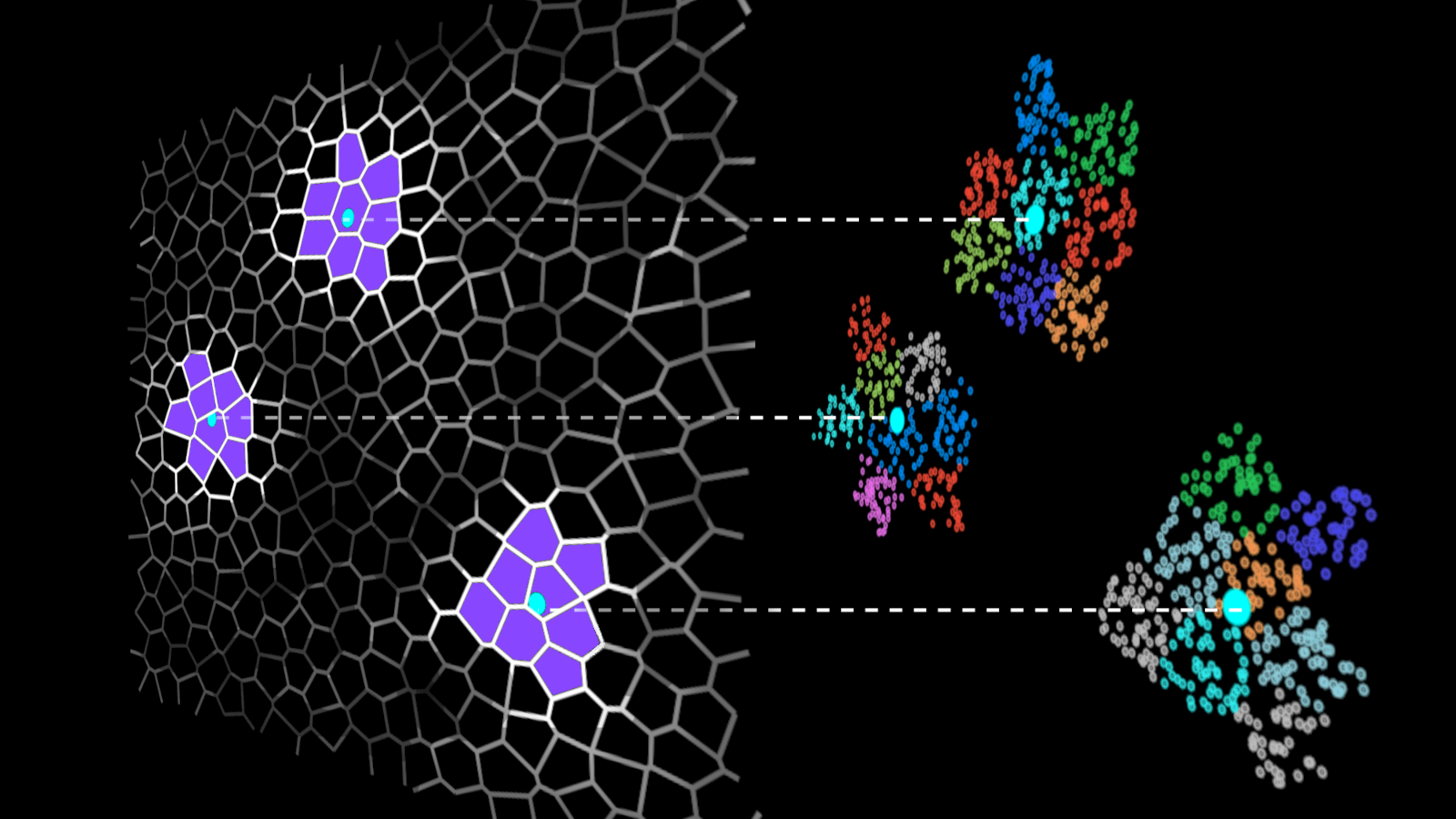
IVF-Flat algorithm
- IVF-Flat algorithm is used to accelerate vector search by grouping dataset vectors into clusters and limiting the search to nearest clusters for each query.
- Before searching the dataset, an index needs to be built which stores the required information for efficient search.
- The index is created by creating an inverted list which contains the indices of vectors belonging to each cluster.
- The most important hyperparameter is the number of clusters to be used.
- The search is performed in two steps, coarse search and fine search.
- Coarse search selects nearby clusters for each query while the fine search compares the query vectors to dataset vectors in the selected clusters.
Adding dataset vectors to the index
- Dataset vectors are assigned to their cluster and added to the appropriate list of vectors in the clusters.
- Index building can be done with automatic data subsampling, using a fraction of the dataset for training the cluster centers.
- The number of clusters can be changed by changing the value of the
n_clusters parameter.
- By default, the cluster centers do not change when new vectors are added to the dataset.
- The pool allocator can be set up to manage memory for clustering and search.
