Rebuilding Netflix Video Processing Pipeline with Microservices
Rebuilding Netflix Video Processing Pipeline with Microservices
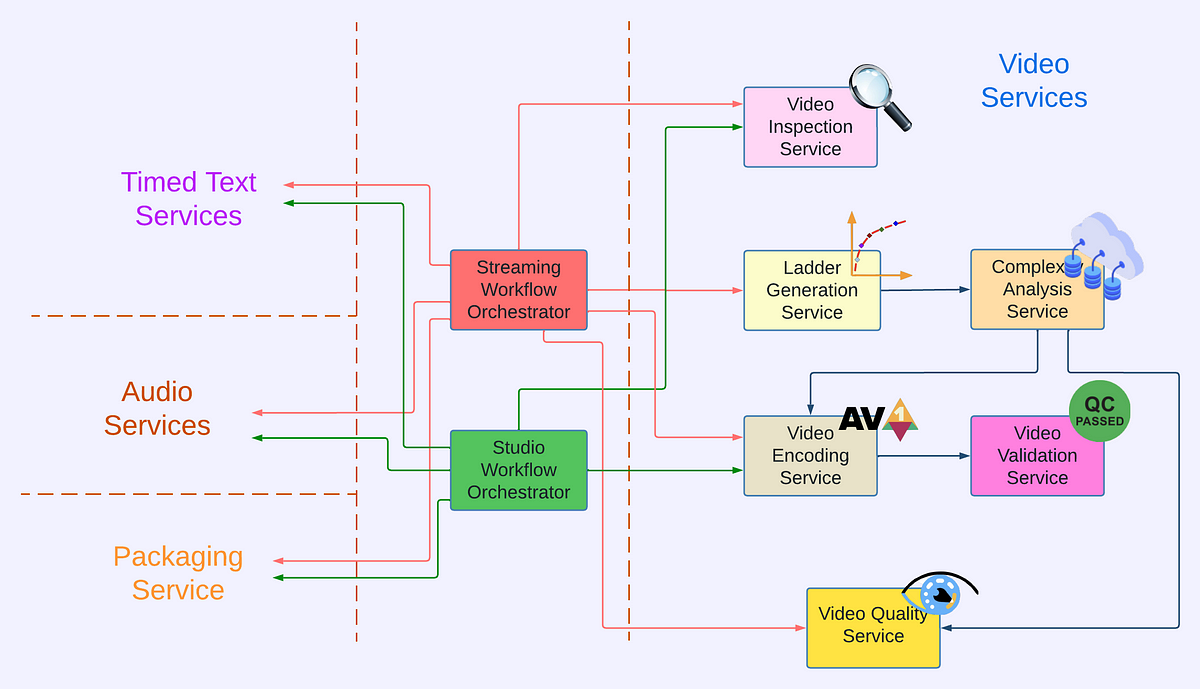
The Video and Image Encoding team in Encoding Technologies (ET) at Netflix has spent the last few years rebuilding the video processing pipeline on their next-generation microservice-based computing platform called Cosmos. This was done to support their studio/content-development use cases, which had different latency and resiliency requirements compared to the traditional streaming use case.
Previously, Netflix used a monolithic system called Reloaded, which led to increased system complexity. To overcome this, they implemented a microservice architecture in Cosmos, where the system is composed of fine-grained services, each focusing on a single functionality. Two independent microservices were created: Video Encoding Service (VES) and Video Quality Service (VQS).
Other services in the video processing pipeline include Video Inspection Service (VIS), Video Validation Service (VVS), and Ladder Generation Service (LGS). These services allow for decoupled functionality and improved flexibility, scalability, and feature development velocity.
The rebuild of the video processing pipeline on Cosmos has been essential for Netflix to continue innovating and supporting their streaming service, as well as their studio partners. The microservice architecture provides efficiency and flexibility, making it critical for Netflix's continued success.